Climate change is driving the largest internal migration in American history. Over 3.2 million Americans have been displaced by floods since 2022 alone, with $1.5 trillion in property losses on the horizon. This paradigm shift in population redistribution is set to reshape socioeconomic patterns, strain real estate markets, and challenge infrastructure. It highlights the urgent need to anticipate future migration to enhance national preparedness and societal well-being.
To that end, AlphaGeo has conducted an in-depth study to forecast migration and settlement patterns over the next 30 years in the U.S., identifying locations that are likely to become climate havens — low risk but also offering quality infrastructure and economic opportunity.
Download Report
Our comprehensive, 17-page report is available for download via the link below.

Key Takeaways:
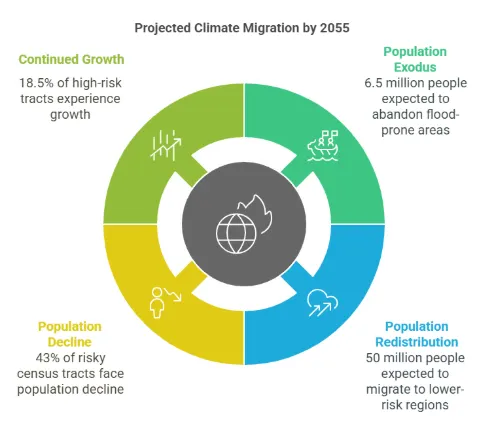
1. Significant populations shifts are expected, with mass flights to safety: By 2055, about 6.5 million people will leave high-risk flood zones, while safer areas will gain an additional 50 million residents.
2. Nevertheless, migration patterns will continue to reflect trade-offs between risk, opportunity, and affordability — not just climate exposure.: Environmental risks are not the only drivers of migration — many high-risk areas will still see growth, as nearly 20% of flood-exposed regions attract new residents driven by jobs, affordability, and other factors that outweigh flood risk in those areas.
3. Migration behavior varies based on risk versus resilience-seeking preferences: AlphaGeo’s climate-adjusted projections reveal contrasts in county-level migration behavior. While 43% of flood-prone census tracts are projected to decline, several high-risk regions (e.g., Florida coast, suburban Louisiana, and affordable resilient counties) are expected to continue growing. This divergence reveals a broader behavioral divide between risk-seeking and resilience-seeking states.
- Florida and Louisiana exemplify risk-seeking behavior — residents continue to move into flood-exposed regions due to economic opportunity and affordability.
- Michigan and North Carolina, by contrast, are resilience-seeking states, attracting migrants to safer, economically stable areas that combine affordability with quality of life.